
- Toolbox Talks
- Guest Post and Backlink

Risk Assessment Procedures
- by Afnan Tajuddin
- Risk assessment
Risk assessment is essential in ensuring safety and well-being in any organization. This process identifies, evaluates, and prioritizes potential risks in a workplace or activity, resulting in safer working environments, accidents prevention, and increasing safety awareness. The five steps to conducting a risk assessment involve identifying the hazard, assessing the risk, implementing controls and safeguards, reassessing the risk with control in place, and confirming the reduced risk. The article provides examples of risk control measures, techniques for effective risk control, and methods for evaluating risks.
Table of Contents
Understanding Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a vital process that every organization must undertake to ensure the safety and well-being of its employees, customers, and the public. It is the process of identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing potential hazards or risks in a workplace or activity. A risk assessment is crucial because it helps organizations understand the level of risk and take appropriate measures to control or eliminate the identified risks.
The basic principles of risk assessment include the identification of hazards, the assessment of risks associated with these hazards, the identification of control measures to mitigate these risks, and the review and monitoring of these control measures.
Benefits of Conducting a Risk Assessment
Conducting a risk assessment provides several benefits to an organization. The primary benefit is the protection of employees and customers from harm. By identifying and controlling potential hazards, organizations can prevent accidents and injuries from occurring.
Conducting a risk assessment also increases safety awareness and promotes a safety culture within an organization. By involving employees in the risk assessment process, they become more aware of potential hazards and how to control them. This results in a safer working environment and reduces the likelihood of accidents and incidents.
In addition, conducting a risk assessment demonstrates legal compliance and due diligence. It is a legal requirement for employers to provide a safe working environment, and conducting a risk assessment is an essential step in fulfilling this requirement. It also helps to reduce insurance premiums, as insurance companies are more likely to offer lower premiums to organizations that have a thorough and effective risk assessment process in place.
5 Steps to Conducting a Risk Assessment
There are 5 steps to conduct a risk assessment:
- Identify the hazard.
- Assess the risk
- Put controls/safe guards in place
- Re-assess the risk with control in place.
- Confirmation of reduced risk.
1. Identify the hazard.
Hazard identification is the process of identifying all hazards at risk in your work environment.
Many hazards exist in the workplace. Some of these can be easily identified such as manual handling , but others are less obvious and may not even show up on accident reports or injury logs. Consider how people work with plant equipment to identify hidden hazards that could cause harm without being detected by existing records (such as a new cleaning solution). Identifying what hazardous substances are used is also important when thinking about potential health risks for workers who use them regularly or come into contact during maintenance operations. For example, many workplaces contain asbestos which poses severe dangers if inhaled over time due to its link to respiratory illnesses like lung cancer.
Four risk categories to be use to identify hazards: Extreme, High, Moderate, and Low.
2. Assess the risk
Once you have identified what hazards may be present. decide how likely it is that someone could be harmed by these and to what extent if so. This is assessing the level of risk for your business premises or workplace environment with regard to those potential hazards. Decide: who might be harmed; what action you’re already taking in order to reduce this harm happening again (control measures); any further steps needed-who will carry out this necessary action; when they need to do it by
Risk matrix ( Risk assessment matrix )
With all the risks that are out there, a risk matrix can be an easy way to assess the risk. The Risk Matrix is an incredible tool for quickly calculating the risk of a project. It helps identify what could go wrong (likelihood) and how much damage it would cause if these outcomes occurred (severity). This makes prioritizing issues quick and simple so you know which ones need attention.
Guidelines for assessing Severity
- Major: Environmental Loss (Major pollution affecting life outside site), People (Fatality or Permanent disability.)
- Serious: Environmental Loss (Major pollution confined to the inside site), People (Long term absence / Offsite treatment)
- Moderate: Environmental Loss (Significant pollution causing a shutdown of units), People (Moderate treatment / Shot term absence)
- Minor: Environmental Loss ( Pollution above limits / Small spills, emissions ), People (First aid case / No significant injury)
Guidelines for assessing Likelihood
- Very unlikely : Little or no chance of occurrence
- Unlikely : Could occur, less than 50 / 50 chance
- Possible : 50 / 50 chance
- Probable : More likely to occur than not more than 50 / 50 chance
Methods for Analyzing Risks
- Qualitative analysis: simple and cost-effective approach that involves identifying and ranking hazards based on their likelihood and severity
- Semi-quantitative analysis: assigns numerical values to the severity and likelihood of risks to calculate a risk score
- Quantitative analysis: involves using statistical methods to quantify the probability of a risk occurring and its potential impact
Risk Evaluation
- Determining whether risk levels are acceptable or unacceptable based on the results of the risk analysis
- Methods for evaluating risks: risk severity matrix, risk priority number, and risk ranking
- Developing controls that reduce risk to an acceptable level, considering the organization’s priorities, resources, and overall business goals
3. Risk Control : Put controls/safe guards in place
1. definition of risk control:.
Risk control refers to the implementation of measures or strategies to mitigate or eliminate the potential risks identified during the risk assessment process.
2. Importance of Risk Control in Risk Assessment:
Risk control is a crucial part of the risk assessment process because it helps to ensure the safety and health of workers and others who may be affected by workplace hazards. Effective risk control measures can prevent accidents, injuries, and illnesses, and can also minimize financial losses and damage to equipment and property.
3. Methods for Controlling Risks: There are several methods for controlling risks in the workplace, including:
- Elimination: Elimination involves completely removing the hazard or risk from the workplace. This may involve replacing hazardous equipment or substances with safer alternatives or modifying work processes to eliminate the risk altogether.
- Substitution: Substitution involves replacing a hazardous substance, material, or process with a less hazardous alternative.
- Engineering Controls: Engineering controls involve designing or modifying equipment, tools, or processes to minimize the risk of exposure to hazardous conditions. Examples include ventilation systems, noise reduction measures, and machine guards.
- Administrative Controls: Administrative controls involve implementing policies and procedures to control the risk of exposure to hazardous conditions. Examples include training programs, job rotation, and work scheduling.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Personal protective equipment ( PPE ) involves providing workers with protective gear to reduce their exposure to hazardous conditions. Examples include hard hats, gloves, respirators, and safety glasses.
4. Techniques for Effective Risk Control: To ensure the effectiveness of risk control measures, it is essential to follow these techniques:
- Involve workers in the risk assessment and control process
- Implement a hierarchy of controls (starting with elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and PPE )
- Regularly review and evaluate risk control measures and adjust them if necessary.
5. Examples of Controls Commonly Used in Workplaces: Examples of common risk control measures in workplaces include:
- Installing guards or barriers around machinery
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE) to workers
- Implementing lockout/tag-out procedures to prevent accidental start-up of machinery
- Using ventilation systems to control exposure to hazardous substances
- Providing training programs to workers to increase their awareness of workplace hazards.
4. Re-assess the risk with control in place
After implementing control measures to reduce or eliminate the identified risks, it is essential to re-assess the risks to ensure that they have been adequately controlled. This involves reviewing the effectiveness of the control measures in place and evaluating whether they have reduced the level of risk to an acceptable level.
To do this, ask yourself the following questions:
- Have the control measures been implemented as planned?
- Have they effectively reduced or eliminated the identified hazards or risks?
- Are there any new hazards or risks that have emerged as a result of the control measures?
- Have the control measures introduced any new risks?
Based on the answers to these questions, you may need to revise the control measures or implement additional ones to further reduce the risks.
5. Confirmation of reduced risk
Confirmation of the reduced risk is a crucial step in the risk assessment process. It involves reviewing the control measures that have been put in place and assessing their effectiveness in reducing or eliminating the identified hazards. This step can be done through a range of methods, including:
- Regular inspections of the workplace to identify any new hazards or potential risks that may have arisen.
- Monitoring the workplace to ensure that the control measures are being implemented correctly.
- Reviewing the incident records to see if there have been any incidents or near misses related to the identified hazards.
- Seeking feedback from employees to identify any issues or concerns related to the control measures in place.
It’s important to regularly review and update the risk assessment to ensure that the control measures remain effective and that any new hazards or risks are identified and addressed promptly. By regularly reviewing the risk assessment, it’s possible to ensure that the workplace remains safe and healthy for all employees.
Who needs to do a risk assessment
The team will be led by the project manager, who is in charge of managing safety for a particular site. The Area Safety Engineer, Shift supervisors, and any other engineer if necessary. should have experience with risk assessment tools like MSHA’s HAZCOM or OSHA’s EH&S Toolkit to ensure they can properly assess risks at construction sites.
When should I do a risk assessment
Risk assessments are an essential step to prevent harm and accidents on site. risk assessment shall be prepared before starting any work & it is required for all activities.
When to Update Risk Assessment
In order to keep up with the ever-changing world, it’s important that you update your risk assessment regularly. In the construction industry, there are many reasons for updating your risk assessment.
Changes to design or materials may demand a new hazard analysis.
After an accident has occurred that requires changes in safety protocol If key equipment changes. Even small company policies updates. A project suspension will also require a constant reassessment of what consequences this would have for workers’ lives. A new subcontractor who join in work process so it’s necessary for any risk assessment need to update too.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Risk Assessment
1. failing to identify all potential hazards:.
- Risk assessments must identify all potential hazards to accurately evaluate the risks.
- Skipping or overlooking some hazards can lead to incorrect risk assessment and ineffective controls.
2. Underestimating the Likelihood or Severity of Harm:
- Assessing the likelihood and severity of harm is critical to effective risk assessment.
- Underestimating these factors can lead to ineffective controls and increased risk exposure.
3. Failing to Implement Appropriate Controls:
- The purpose of risk assessment is to identify the appropriate controls to reduce risk.
- Not implementing the appropriate controls or implementing ineffective controls can result in unnecessary risk.
4. Failing to Review and Update Assessments Regularly:
- Risk assessments must be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that controls remain effective.
- Failing to do so can result in outdated assessments and ineffective controls.
5. Examples of Common Mistake:
- Failing to identify all potential hazards: A warehouse risk assessment fails to identify the risk of slips and falls from a wet floor.
- Underestimating the likelihood or severity of harm: A machine operator fails to recognize the potential danger of a malfunctioning machine.
- Failing to implement appropriate controls: A company identifies the hazard of a chemical spill but fails to implement proper storage and handling procedures.
- Failing to review and update assessments regularly: A construction company conducts a risk assessment for a new project but fails to review and update the assessment as the project progresses.
6. Techniques for Avoiding Common Mistakes:
- Use a comprehensive hazard checklist to identify all potential hazards.
- Use objective criteria to assess the likelihood and severity of harm.
- Use the hierarchy of controls to identify the most effective controls for the identified hazards.
- Establish a regular review schedule and ensure that assessments are updated as necessary.
Challenges of Conducting a Risk Assessment
- Lack of resources: Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment requires adequate resources such as time, funding, and personnel. Inadequate resources can lead to a rushed or incomplete risk assessment, which may miss crucial risks or hazards.
- Lack of knowledge and expertise: Conducting a risk assessment requires a certain level of expertise and knowledge. Without it, identifying potential hazards and assessing risks can be challenging, leading to inaccurate assessments and inadequate risk management.
- Difficulty in identifying all potential hazards and risks: It can be challenging to identify all potential hazards and risks in a complex work environment. Some risks may not be apparent, and others may be overlooked, leading to incomplete or inaccurate risk assessments.
- Resistance to change: Conducting a risk assessment may require changes in the work environment, work practices, and procedures, which may be met with resistance from employees or management. This can make it challenging to implement and maintain a risk management plan.
- Changing work environment: Work environments are continually changing, and risk assessments must be updated accordingly. This can be a challenge, particularly in industries with rapidly evolving technologies, processes, or equipment. Failure to keep up with these changes can lead to outdated or inaccurate risk assessments.
Tools and Resources for Conducting Risk Assessment
1. risk assessment templates.
- Templates are pre-designed forms that can help to streamline the risk assessment process
- They provide a framework for identifying and assessing risks in a consistent manner
- Templates can be customized to fit the specific needs of an organization
2. Online Risk Assessment Software
- Online software can be used to conduct and manage risk assessments
- They provide a centralized location for storing risk assessment data
- Some software can automate the risk assessment process, including generating reports and recommending controls
3. Government Resources and Guidelines
- Governments often provide resources and guidelines for conducting risk assessments
- These resources can be a valuable source of information on best practices and legal requirements
- Examples of government resources include the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ) in the United States and the Health and Safety Executive ( HSE ) in the United Kingdom
4. Other Useful Tools and Resources
- There are many other tools and resources available for conducting risk assessments, such as checklists and decision-making frameworks
- Organizations can also seek the expertise of consultants or industry associations for guidance on conducting risk assessments
5. Examples of Successful Use of Tools and Resources
- A manufacturing company successfully used a risk assessment template to identify hazards in their production process and implement appropriate controls
- An online retailer used risk assessment software to centralize their risk assessment data and automate the process of generating reports for regulatory compliance
- A construction company used government resources and guidelines to ensure compliance with legal requirements and improve their safety record.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply.


A complete guide to the risk assessment process
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 7 min
Mark Zuckerberg, the founder of Facebook, once said, “The biggest risk is not taking any risk. In a world that's changing really quickly, the only strategy that is guaranteed to fail is not taking risks.”
While this advice isn't new, we think you’ll agree that there are some risks your company doesn’t want to take: Risks that put the health and well-being of your employees in danger.
These are risks that aren’t worth taking. But it’s not always clear what actions, policies, or procedures are high-risk.
That’s where a risk assessment comes in.
With a risk assessment, companies can identify and prepare for potential risks in order to avoid catastrophic consequences down the road and keep their personnel safe.
What is risk assessment?
During the risk assessment process, employers review and evaluate their organizations to:
- Identify processes and situations that may cause harm, particularly to people (hazard identification).
- Determine how likely it is that each hazard will occur and how severe the consequences would be (risk analysis and evaluation).
- Decide what steps the organization can take to stop these hazards from occurring or to control the risk when the hazard can't be eliminated (risk control).
It’s important to note the difference between hazards and risks. A hazard is anything that can cause harm , including work accidents, emergency situations, toxic chemicals, employee conflicts, stress, and more. A risk, on the other hand, is the chance that a hazard will cause harm . As part of your risk assessment plan, you will first identify potential hazards and then calculate the risk or likelihood of those hazards occurring.
The goal of a risk assessment will vary across industries, but overall, the goal is to help organizations prepare for and combat risk. Other goals include:
- Providing an analysis of possible threats
- Preventing injuries or illnesses
- Meeting legal requirements
- Creating awareness about hazards and risk
- Creating an accurate inventory of available assets
- Justifying the costs of managing risks
- Determining the budget to remediate risks
- Understanding the return on investment
Businesses should perform a risk assessment before introducing new processes or activities, before introducing changes to existing processes or activities (such as changing machinery), or when the company identifies a new hazard.
The steps used in risk assessment form an integral part of your organization’s health and safety management plan and ensure that your organization is prepared to handle any risk.
Preparing for your risk assessment
Before you start the risk management process, you should determine the scope of the assessment, necessary resources, stakeholders involved, and laws and regulations that you’ll need to follow.
Scope: Define the processes, activities, functions, and physical locations included within your risk assessment. The scope of your assessment impacts the time and resources you will need to complete it, so it’s important to clearly outline what is included (and what isn’t) to accurately plan and budget.
Resources : What resources will you need to conduct the risk assessment? This includes the time, personnel, and financial resources required to develop, implement, and manage the risk assessment.
Stakeholders: Who is involved in the risk assessment? In addition to senior leaders that need to be kept in the loop, you’ll also need to organize an assessment team. Designate who will fill key roles such as risk manager, assessment team leader, risk assessors, and any subject matter experts.
Laws and regulations: Different industries will have specific regulations and legal requirements governing risk and work hazards. For instance, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets and enforces working condition standards for most private and public sectors. Plan your assessment with these regulations in mind so you can ensure your organization is compliant.
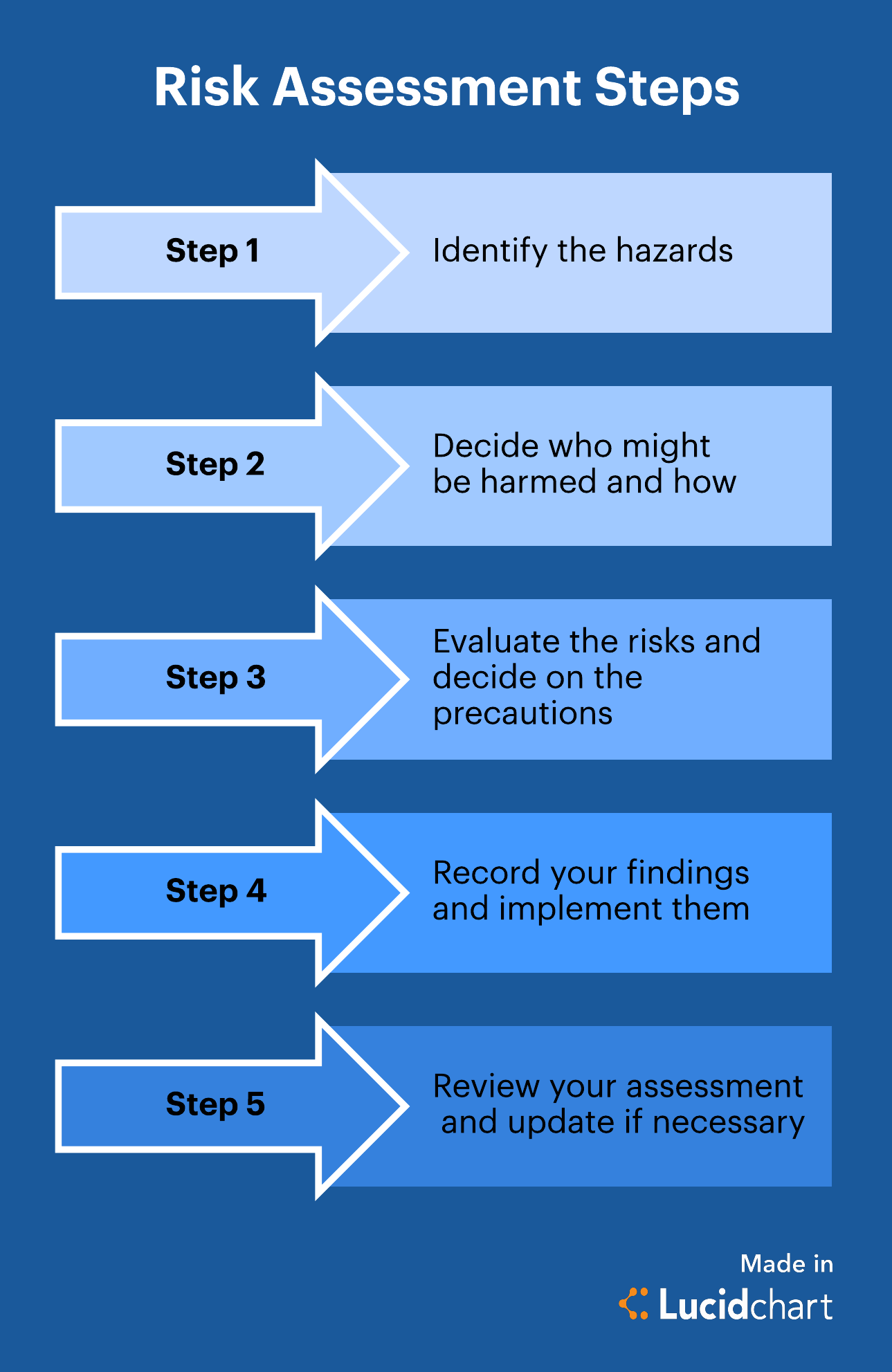
5 steps in the risk assessment process
Once you've planned and allocated the necessary resources, you can begin the risk assessment process.
Proceed with these five steps.
1. Identify the hazards
The first step to creating your risk assessment is determining what hazards your employees and your business face, including:
- Natural disasters (flooding, tornadoes, hurricanes, earthquakes, fire, etc.)
- Biological hazards (pandemic diseases, foodborne illnesses, etc.)
- Workplace accidents (slips and trips, transportation accidents, structural failure, mechanical breakdowns, etc.)
- Intentional acts (labor strikes, demonstrations, bomb threats, robbery, arson, etc.)
- Technological hazards (lost Internet connection, power outage, etc.)
- Chemical hazards (asbestos, cleaning fluids, etc.)
- Mental hazards (excess workload, bullying, etc.)
- Interruptions in the supply chain
Take a look around your workplace and see what processes or activities could potentially harm your organization. Include all aspects of work, including remote workers and non-routine activities such as repair and maintenance. You should also look at accident/incident reports to determine what hazards have impacted your company in the past.
Use Lucidchart to break down tasks into potential hazards and assets at risk—try our free template below.
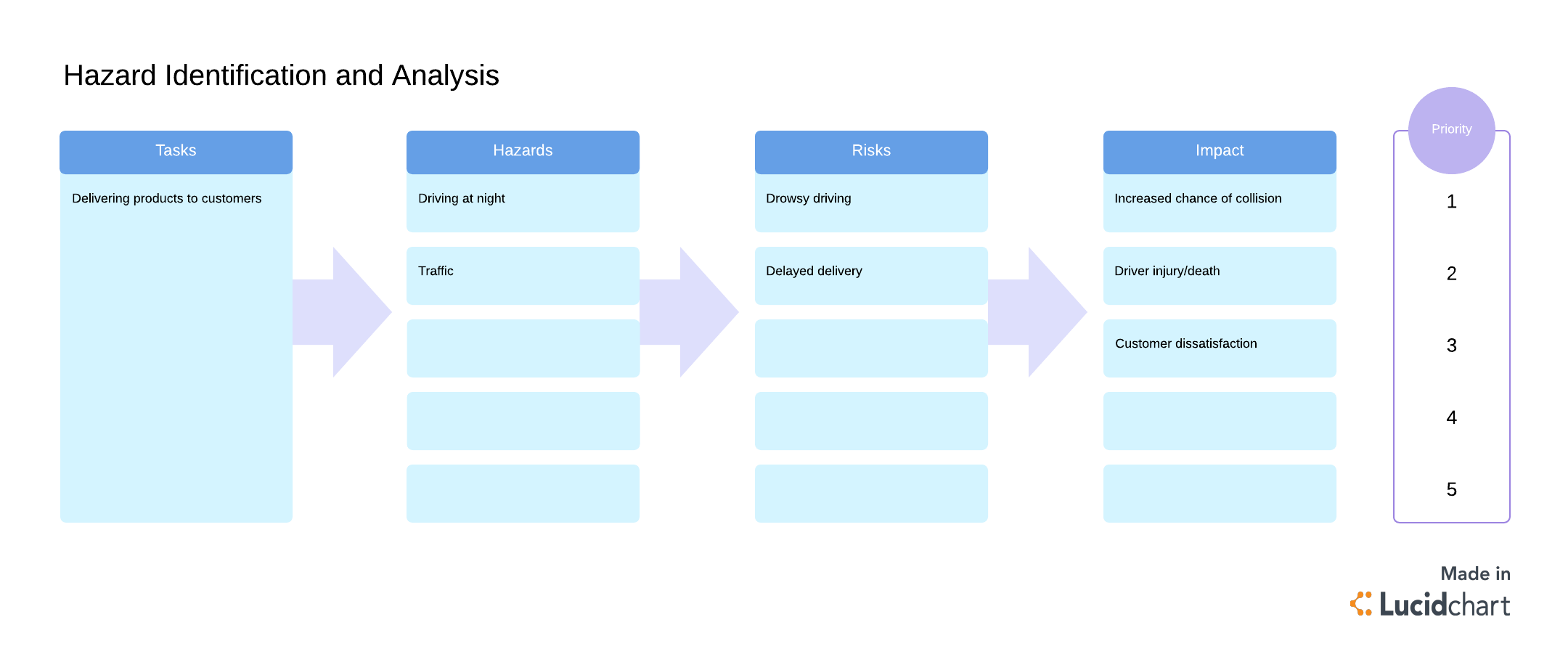
2. Determine who might be harmed and how
As you look around your organization, think about how your employees could be harmed by business activities or external factors. For every hazard that you identify in step one, think about who will be harmed should the hazard take place.
3. Evaluate the risks and take precautions
Now that you have gathered a list of potential hazards, you need to consider how likely it is that the hazard will occur and how severe the consequences will be if that hazard occurs. This evaluation will help you determine where you should reduce the level of risk and which hazards you should prioritize first.
Later in this article, you'll learn how you can create a risk assessment chart to help you through this process.
4. Record your findings
If you have more than five employees in your office, you are required by law to write down your risk assessment process. Your plan should include the hazards you’ve found, the people they affect, and how you plan to mitigate them. The record—or the risk assessment plan—should show that you:
- Conducted a proper check of your workspace
- Determined who would be affected
- Controlled and dealt with obvious hazards
- Initiated precautions to keep risks low
- Kept your staff involved in the process
5. Review your assessment and update if necessary
Your workplace is always changing, so the risks to your organization change as well. As new equipment, processes, and people are introduced, each brings the risk of a new hazard. Continually review and update your risk assessment process to stay on top of these new hazards.
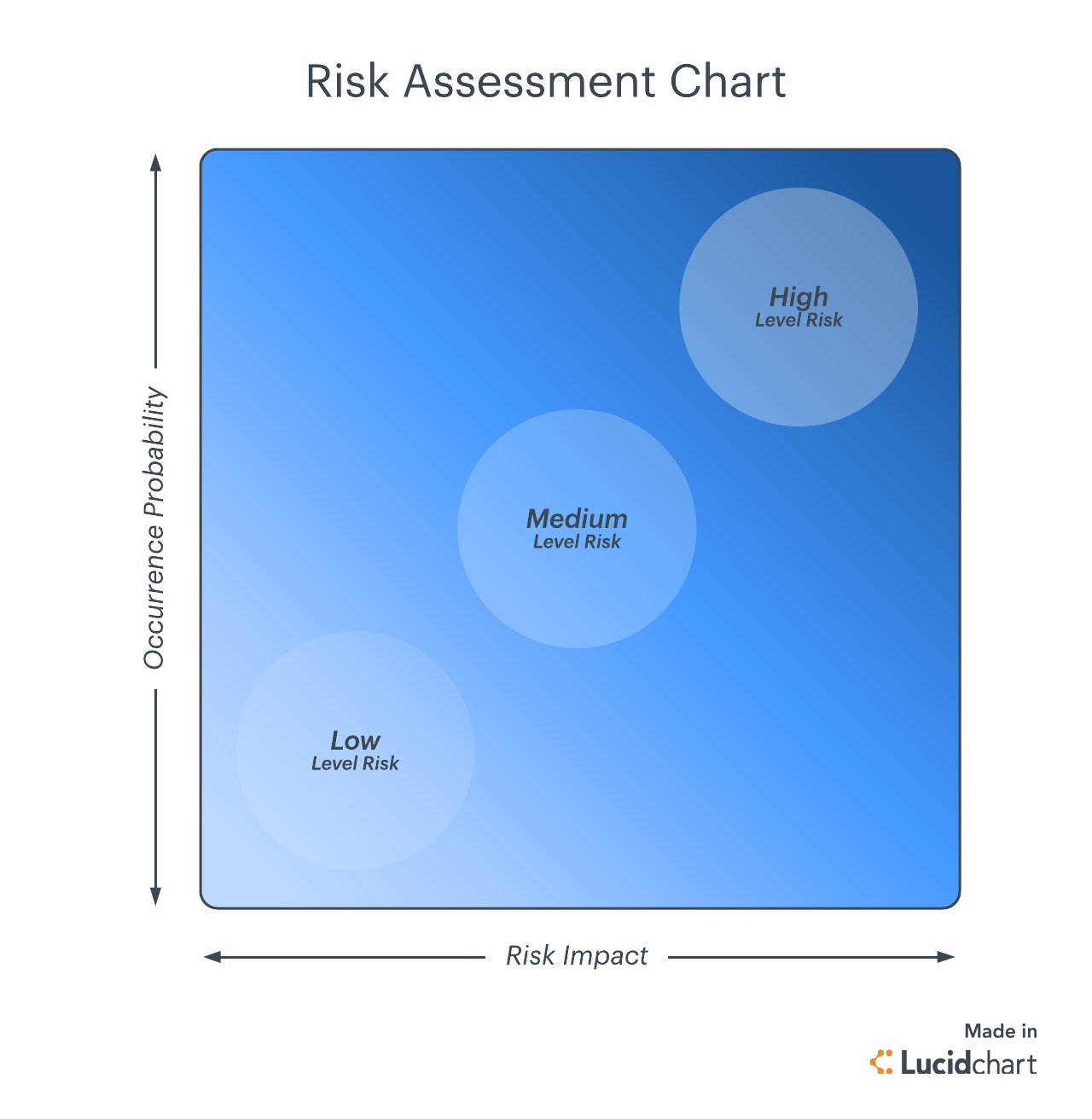
How to create a risk assessment chart
Even though you need to be aware of the risks facing your organization, you shouldn’t try to fix all of them at once—risk mitigation can get expensive and can stretch your resources. Instead, prioritize risks to focus your time and effort on preventing the most important hazards. To help you prioritize your risks, create a risk assessment chart.
The risk assessment chart is based on the principle that a risk has two primary dimensions: probability and impact, each represented on one axis of the chart. You can use these two measures to plot risks on the chart, which allows you to determine priority and resource allocation.
Be prepared for anything
By applying the risk assessment steps mentioned above, you can manage any potential risk to your business. Get prepared with your risk assessment plan—take the time to look for the hazards facing your business and figure out how to manage them.

Now it's time to create your own risk management process, here are five steps to get you started.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
5 steps to any effective risk management process.
While you can’t entirely avoid risk, you can anticipate and mitigate risks through an established risk management process. Follow these steps!
5 steps of the strategic planning process
Implement the strategic planning process to make measurable progress toward achieving your company’s vision and make decisions that will keep you on the path to success for years to come.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
- Browse Our Solutions
- Business Intelligence
- Implementation & Support
- Incident Management
- Risk Management
- Audit & Inspections
- Contractor Safety
- Chemical Management
- SDS Management
- Behavioural Based Safety
- Asset Register
- Digital Procedural Walkthrough
- Shift Handover
- Journey Planning
- Compliance & Obligations
- Training Management
- Microlearning
- EHS Training Content Library
- Environmental Compliance
- Environmental Permit
- Waste Management
- Emission Management
- Occupational Health
- Industrial Hygiene
- Case Management
- Drug & Alcohol Testing
- Ergonomic Assessment
- Psychosocial Management
- Risk Analysis and Control Management
- Emergency Preparedness Response
- Control of Work
- Management of Change
- Permit to Work
- Process Hazard Analysis
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
- Metrics & Materiality
- Regulatory and Compliance
- Business Planning
- Stakeholder Management
- Why Evotix?
- Customer Stories
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Transportation and Logistics
- Local Authority/Housing
- Energy and Utilities
- Mining and Metals
- Oil and Gas
- Warehousing
- Food & Drink
- Two Bald Guys Talking Safety
- Resource Library
- News & Press
- Events & Webinars
- Work at Evotix
- Book a Demo

5 Types of Risk Assessment & How to Use Them
29 October 2024 - Evotix
Risk assessments are often a legal requirement, essential for ensuring workplace safety and compliance. Simply put, a risk assessment helps identify hazards and potential risks within a work environment, providing effective strategies to mitigate or eliminate these threats, ultimately promoting a safe and secure workplace for everyone.
Hazards in the workplace vary widely, from physical dangers to chemical exposures and beyond—so risk assessments must be adaptable to address these different challenges. Using the correct type of risk assessment for each situation is key to capturing the unique risks that exist within any given workplace. Often, a blend of multiple assessment types provides the most thorough and effective evaluation, allowing you to pull the most relevant aspects from each into one cohesive approach.
In this guide, we’ll explore the five main types of risk assessments and how you can use them to support comprehensive health and safety management in your organization.
Stages of a risk assessment
To ensure that your risk assessment is effective and comprehensive, it should encompass the following six key steps:
1. Plan
Good planning is integral to ensuring you get your risk assessment off to a strong start. Before conducting your risk assessment, consider these four elements noted by OSHA:
What are you assessing? (A piece of equipment, process or workplace area?)
What resources do you need to carry out the assessment ? (Tools or equipment?)
Who is involved? (Workers, managers, supervisors or suppliers?)
What laws, regulations and internal policies do you need to comply with?
2. Identify hazards
This involves a walkthrough of your workspace to identify anything that could reasonably be expected to cause harm. Involving other employees in this stage could be helpful, as they may have noticed things that don’t immediately stick out at you.
While assessing the workplace, ensure you consider long-term hazards to health (like high noise levels or exposure to harmful substances) and safety hazards.
Once you’ve identified each hazard, make sure you understand how it could harm someone or the environment – as this will help you identify the most impactful way of managing the risk further down the line.
3. Evaluate identified risks
Now that hazards have been identified, it’s time to decide how to handle them.
Under the OSH Act , employers are obligated to maintain workplaces that are free from known hazards that could pose risks to their employees. One of the most effective strategies to achieve this is by benchmarking your current practices against industry best standards.
First, assess the controls you currently have in place and how they’re implemented. Compare these controls against identified best practices to see if there’s room for improvement.
4. Take action
Once you’ve identified specific areas for improvement to reduce risks, it's time to act. HSE suggests applying the following principles:
Try a less risky option (for example, switching to a less hazardous chemical)
Prevent access to the hazard (such as guarding)
Organize work to reduce exposure to the hazard (for example, by placing barriers between pedestrians and traffic)
Issue personal protective equipment (gloves, goggles, etc)
Provide emergency areas (like first aid or eye wash stations)
5. Record findings and actions taken
At this stage, you should write down the risk assessment results and share them across your organization to encourage all employees to put these new actions into practice.
Write down your results as simply as possible, for example: “ Fire door blocked: area cleared, staff instructed, weekly checks.”
While recording your risk assessment findings, you should be able to demonstrate:
That you've identified the hazards
That you’ve decided who could be harmed
How you plan to eliminate/minimize the risks and hazards
6. Review process
Workplaces are constantly evolving, with new processes introducing new risks and hazards. Therefore, it’s essential to regularly review your practices and update the relevant risk assessment forms as needed.
What are the different types of risk assessment?
Risk assessments come in many different forms, but here are the five most common:
1. Qualitative risk assessment
Qualitative risk assessments are the most frequently used risk assessments for companies in high-risk industries. Assessments of this kind measure the severity of a risk. In most cases, qualitative risk assessments are used to determine the severity of multiple risks at once. These assessments rely on the perceptions and judgments of an individual—often an expert in the company’s field or a member of management.
When these assessments are employed, the assessor’s personal experience, observations and interviews are used to gather qualitative data, which are then analyzed with the goal of determining the severity of multiple risks.
The severity of a risk can be determined using the following formula: impact describes how severely a risk could negatively affect a project and likelihood describes how often the risk is likely to occur.
Severity = Impact x Likelihood
When the information is presented, it is organized either into categories or a graph known as a Qualitative Risk Assessment Matrix. Both schemes are based on severity. Categories are labeled High , Medium and Low —or, depending on the company’s preferences, Green , Amber and Red (GAR). In a Qualitative Assessment Matrix, one axis is labeled ‘Impact’ and the other ‘Likelihood,’ and plot points (risks) are charted in according to severity. Presentations allow the company to quickly identify the highest-severity risks.
When compared to quantitative risk assessments, qualitative risk assessments can often be more practical. These assessments are cheaper and faster and allow for the comparative analysis of multiple risks. They don’t require gathering vast amounts of numerical data; instead, qualitative risk assessments rely only on the judgments of one person. Most importantly, qualitative risk assessments enable companies to invent solutions for the most severe risks quickly and efficiently.
2. Quantitative risk assessment
A quantitative risk assessment involves determining the severity and likelihood of a risk by giving it a number. This type of assessment aims to gauge how much the impact of the risk will cost an organization. Rather than referring to a risk as high, medium or low, a quantitative risk assessment assigns a digit to the risk.
The main difference between a qualitative and quantitative risk is that rather than being based on a person’s judgment, as a qualitative risk is, a quantitative risk analysis relies on hard data. Another contrast between the two is how each process values risk . While in a qualitative risk assessment, an innocuous risk may be rated 'low,' the same risk will be given a low percentage in a quantitative assessment to indicate the possibility of it occurring or causing harm.
A scenario in which quantitative risk assessments are commonly used is to predict the likelihood of a fire or explosion when using harmful chemicals. Project managers can select one of the following methods for quantitative risk assessment:
Failure Mode and Effects Analytics (FMEA) - anticipating shortcomings in business processes and coming up with ways to mitigate their impact on customers
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) - identifies and evaluates impact of natural disasters and sets aside investment in recovery, prevention and mitigation strategies for organizations effected
Expected Monetary Value (EMV) - this method involves senior management carrying out the following equation: Probability in % of Risk Occurring x Cost of Impact in Preferred Currency
Results can also be recorded in a risk assessment matrix (or any other form of an intuitive graphical report) to communicate outstanding hazards to stakeholders. Although this method involves the assignment of numbers to the degree of risk, it is technically a qualitative method in that it's based on the assessor’s judgment.
3. Generic risk assessment
Generic risk assessments include assessing a broad range of specific workplace activities. Generic risk assessments are most useful regarding repetitive tasks which are consistent in application for organizations, such as:
Working in confined spaces
Working at heights
Fire emergency responses
Manual handling
Use of different pieces of machinery
Use of display equipment
Carrying out generic risk assessments in these circumstances often proves useful for large organizations, as the findings can then be applied equally to similar tasks across different areas of the workplace or different sites altogether.
This can be done, for example, with the act of locking out a piece of machinery commonly used across several areas of a manufacturing site or installing electrical equipment.
4. Site-specific risk assessment
As the name suggests, a site-specific assessment places a particular site, environment and team of employees performing the task under the microscope to ensure everything is running as safely as it should be.
The main difference between generic and site-specific assessments is that generic assessments focus on common hazards related to routine activities, like roofing work, while site-specific assessments address unique hazards in a particular location with tailored controls—for instance, valley gutters on a roofing site.
Given the connection between both assessments on a roofing site, it often makes sense to follow a generic assessment with a site-specific one, allowing inspectors or management to focus more closely on specific areas of concern.
Other examples of hazards that could be picked up by a site-specific risk assessment that wouldn’t otherwise be recognized by a generic risk assessment on roofing works include potential asbestos from cement roof sheets or glazing rope or trip hazards, including lightning conductors or drain vents.
5. Dynamic risk assessment
A dynamic risk assessment evaluates risks in rapidly changing, uncertain and often high-risk environments. In contrast to formal risk assessments, which are a legal requirement and should be carried out as a precursor to any task being done, dynamic risk assessments are normally carried out by a lone worker when they arrive in a new environment. There may also be circumstances where a person’s regular working environment changes, making generic or even site-specific risk assessments obsolete and presenting the need for a dynamic approach.
It’s important that the person carrying out a dynamic assessment understands that not every risk can be prepared for because of the nature of these environments. It would be expected that the person conducting a dynamic risk assessment has the experience required to make an informed judgment call if a situation becomes too dangerous – such as delaying a task until safe equipment is sourced.
An example of a dynamic risk assessment includes a construction worker visiting a new worksite and assessing the hazards he hasn’t seen before, having not been on that site. Not to be mistaken as a replacement for formal risk assessments, dynamic risk assessments are to be carried out alongside them to identify any unknown risks.
How Evotix can help
While manual risk assessments are possible, they’re often inefficient for proactive hazard management across an organization. Using software streamlines the process by managing data from all areas of the organization in one place. The software highlights high-risk activities through matrices, enabling rapid control implementation and action tracking to ensure controls are effective. With centralized form storage, it allows workers across departments to conduct and review assessments, keeping everyone informed about hazards. Understanding different types of risk assessments is essential for a safe, productive workplace. Involve employees in the process to ensure they stay updated on solutions for completing tasks safely.
Want to learn more about how we can help streamline your risk management processes?

RELATED BLOGS

7 Benefits of Conducting a Risk Assessment
1 November 2024 - Evotix
Risk assessments aren’t just about clipboards and checking boxes; they bring real, irreplaceable value to the workplace by helping identify current and potential hazards and risks in the workplace..

What is a Risk Assessment?
20 October 2022 - Evotix
So first things first, what exactly is a risk assessment?

Exploring the Role of Industrial Hygiene Software in Risk Mitigation
3 July 2024 - Evotix
Modern workplaces can be hazardous environments. The introduction of new chemicals, tools or practices show that hazards and risks in the workplace are constantly evolving. The challenge is to stay a..
[Trustpilot reviews]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is a Risk Assessment? A risk assessment is a systematic process used to identify potential hazards and risks in a situation, then analyze what would happen should these hazards take place.
The five steps to conducting a risk assessment involve identifying the hazard, assessing the risk, implementing controls and safeguards, reassessing the risk with control in place, and confirming the reduced risk. The article provides examples of risk control measures, techniques for effective risk control, and methods for evaluating risks. 1.
Determine the risk context and scope, then design the risk management strategy. Choose the responsible and related partners, identify the risk and prepare the risk registers. Perform qualitative risk analysis and select the risk that needs detailed analysis. Perform quantitative risk analysis on the selected risk.
What is risk assessment? During the risk assessment process, employers review and evaluate their organizations to: Identify processes and situations that may cause harm, particularly to people (hazard identification). Determine how likely it is that each hazard will occur and how severe the consequences would be (risk analysis and evaluation).
We will delve into the diverse realm of risk assessment methodologies, exploring various approaches that organizations employ to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential threats.
In this guide, we’ll explore the five main types of risk assessments and how you can use them to support comprehensive health and safety management in your organization. To ensure that your risk assessment is effective and comprehensive, it should encompass the following six key steps: 1. Plan.